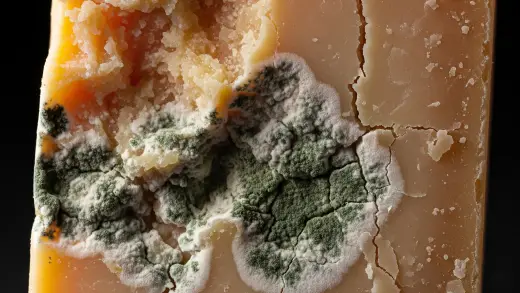
Yes, your cheese can go bad even if you keep it in the fridge. The fridge helps it last longer, but it won’t stay good forever. How long your cheese stays good depends on what kind of cheese it is and how you store it. If you’ve opened it, it will spoil faster. You’ll know it’s gone bad if you see mold (unless it’s a moldy cheese!), it smells funny, or the texture changes.
Did you know that cheese is one of the most popular foods around the world? But many of us aren’t sure how long it will stay good in the fridge. Whether you like sharp cheddar, creamy brie, or tangy feta, you’ve probably wondered if cheese can go bad. The answer is yes, it can!
But here’s the good news: if you store it right, you can keep your cheese fresh and tasty for a much longer time.
The lifespan of cheese depends on several factors, including the type of cheese, how it’s stored, and even how it’s handled before it reaches your fridge.
Let’s dive into the article to understand those factors and how to maximize the self-life of cheese.

What Factors Influence Cheese Shelf Life?
Several factors play a crucial role in determining how long cheese remains fresh and enjoyable. These factors can be broadly categorized into intrinsic (inherent to the cheese itself) and extrinsic (related to the storage environment).
Here are some factors that influence how long your cheese will stay fresh:
Type of Cheese
Some cheeses, like hard cheeses like cheddar or Parmesan, naturally last longer than soft cheeses like Brie or Camembert.
How it’s Made
The way the cheese is made, like if it’s pasteurized or not, can affect how long it stays good.
How it’s Stored
- Moisture Content: Higher moisture content leads to faster spoilage.
- Fat Content: Higher fat content can sometimes contribute to shorter shelf life.
- Rind Type: Washed-rind cheeses may have shorter shelf lives than bloomy-rind cheeses.
- Storage Temperature: Consistent refrigeration (below 40°F/4°C) is crucial.
- Proper Wrapping: Prevents drying out and mold growth.Wrapping: Wrapping it properly, like in cheese paper or plastic wrap, helps keep out air and moisture.
- Location: Keep it away from strong-smelling foods in the fridge.
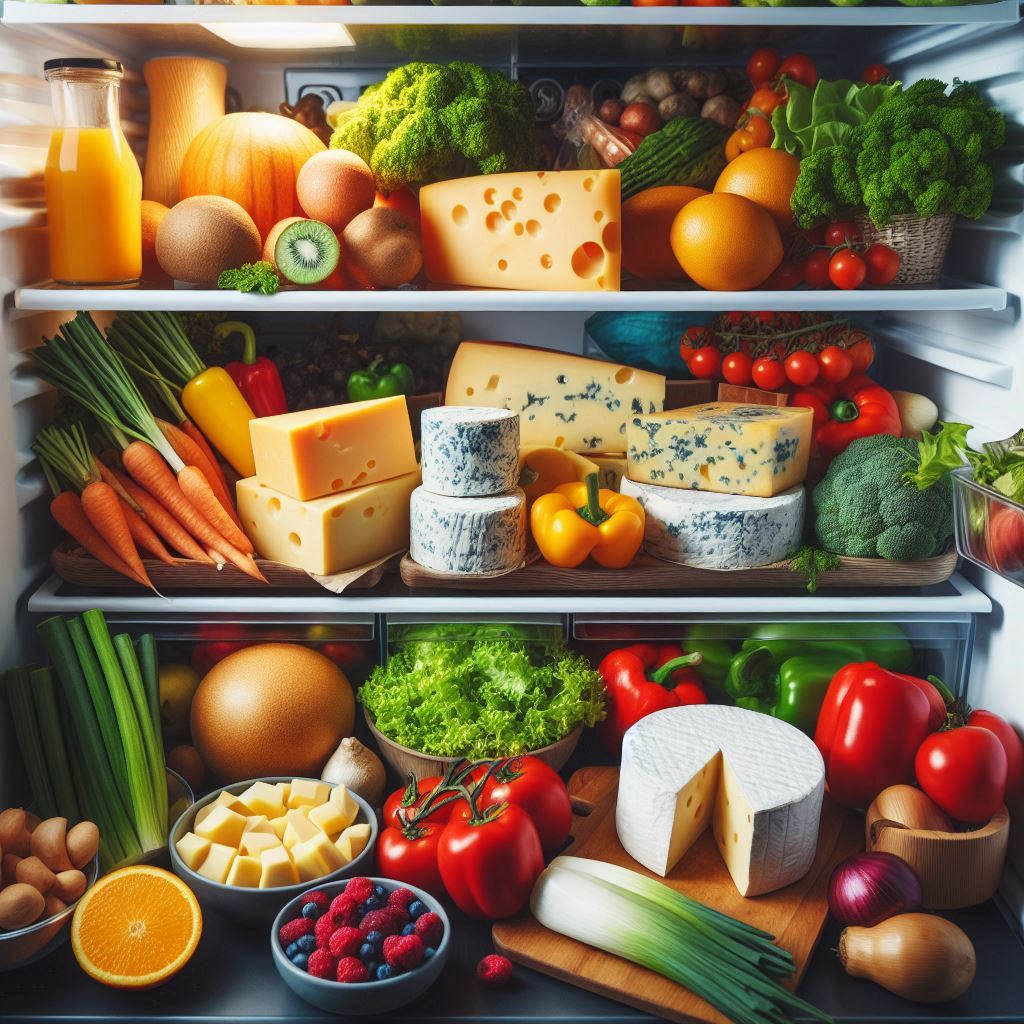
What are the Optimal Storage Techniques for Cheese?
Cheese is a delicious and versatile food, but proper storage is essential to maintain its quality and flavor. Storing cheese correctly not only prevents spoilage but also ensures that you can enjoy its full potential. Let’s explore the optimal storage techniques to keep your cheese at its best.
Temperature Control:
Refrigerate consistently: Most cheeses thrive in a cool environment, typically between 34°F and 38°F (1°C and 3°C).
Avoid temperature fluctuations: Sudden changes in temperature can cause the cheese to dry out, become moldy, or develop off-flavors.
Optimal Placement:
Avoid the refrigerator door: The door experiences frequent temperature changes due to opening and closing, making it an unsuitable location for cheese storage.
Consider the crisper drawer: For some cheeses, the crisper drawer can provide slightly higher humidity, helping prevent drying. However, be mindful of strong-smelling fruits and vegetables that might impart unwanted flavors to the cheese.
Proper Wrapping:
Breathable options: Use cheese paper, parchment paper, or wax paper to allow the cheese to “breathe” while preventing moisture loss and odor absorption.
Limit plastic wrap: Use sparingly, as it can trap moisture and promote mold growth.
Regular Checks:
Monitor for spoilage: Regularly inspect your cheese for any signs of mold, discoloration, or off-odors.
Discard promptly: If you notice any signs of spoilage, discard the affected portion or the entire cheese to prevent further contamination.

What are the Best Ways to Wrap Cheese?
Choosing the right wrapping for your cheese is crucial to keeping it fresh and flavorful. The wrong method can lead to drying, mold growth, or even unwanted flavor absorption.
Breathable Options
Wax Paper/Parchment Paper: These allow the cheese to “breathe,” preventing moisture buildup while minimizing drying.
Cheese Paper: Specifically designed for optimal cheese storage, offering breathability and moisture control.
Limited Use
Plastic Wrap: Use sparingly, as it can trap moisture and lead to off-flavors. It’s best for short-term storage or when combined with breathable options.
Avoid
Airtight Containers: These can promote mold growth by trapping moisture.
Remember: The ideal wrapping method depends on the type of cheese. Soft cheeses may benefit from slightly more protection, while hard cheeses require more breathability.
How Do I Know if My Cheese Has Spoiled?
It’s easy to get attached to a delicious wedge of cheese, but knowing when it’s time to say goodbye is crucial for food safety. Here’s how to spot the signs of spoiled cheese:
- Mold: The most obvious sign is the presence of mold. While some cheeses, like blue cheese, have intentional mold cultures, unexpected mold growth on other cheeses usually indicates spoilage.
- Discoloration: Look for unusual color changes, such as green, blue, or gray patches.
- Slimy Texture: A slimy or sticky surface is a strong indicator of bacterial growth.
- Off-Odors: Spoiled cheese often emits unpleasant odors, such as ammonia, sour milk, or a musty smell.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s best to discard the cheese to avoid the risk of foodborne illness.
Can I Freeze Cheese to Extend Its Shelf Life?
Freezing can be an effective method for extending the shelf life of certain types of cheese, particularly hard cheeses. However, it’s important to note that freezing can affect the texture and flavor of some cheeses.
Suitable Cheeses
Hard Cheeses: Cheeses like cheddar, Parmesan, and Swiss generally freeze well.
Avoid Soft Cheeses: Soft cheeses, such as Brie, Camembert, and cream cheese, tend to become grainy and lose their delicate texture when frozen.
Freezing Techniques
Proper Wrapping: Wrap the cheese tightly in airtight freezer-safe bags or plastic wrap to prevent freezer burn and moisture loss.
Freezing Temperature: Store the wrapped cheese in the coldest part of your freezer, ideally at 0°F (-18°C) or below.
Thawing: Thaw the cheese slowly in the refrigerator. Avoid thawing at room temperature, as this can promote bacterial growth.
Considerations
Texture Changes: Frozen and thawed cheese may have a slightly crumbly or grainy texture.
Flavor Loss: Some cheeses may experience a slight loss of flavor after freezing.
Best Before Freezing: Freeze cheese as soon as possible after purchasing for the best quality.
Remember: While freezing can extend the shelf life of certain cheeses, it’s always best to enjoy cheese fresh for optimal flavor and texture.
FAQs
How do you know if the cheese is spoiled?
Signs of spoiled cheese include mold, unusual odors (like ammonia or sour milk), discoloration, and a slimy texture. When in doubt, discard it.
How long will cheese last in the refrigerator?
Hard cheeses (Cheddar, Parmesan) can last 3-4 weeks in the refrigerator after opening. Soft cheeses (Brie, Camembert) typically last 7-10 days. Fresh cheeses (Ricotta, Cottage Cheese) have a shorter shelf life of 1-2 weeks.
Can you eat expired cheese in the fridge?
No, it’s not recommended. Even if it looks okay, expired cheese can harbor bacteria and cause foodborne illness. Always check for signs of spoilage like mold, discoloration, and off-odors. When in doubt, discard it.
Can cheese go bad without mold?
Yes, cheese can go bad without visible mold. Bacteria can still grow and cause spoilage, leading to unpleasant odors, off-flavors, and potentially harmful toxins. Always check for signs like discoloration, slimy texture, and unusual odors, even if there’s no mold.
Does cheese still age in the fridge?
Yes, cheese continues to age in the refrigerator, but at a slower rate than at room temperature. This aging can affect its flavor and texture over time.
Conclusion
Properly storing cheese is essential for preserving its quality, flavor, and safety. Keep your cheese refrigerated at a consistent temperature between 34°F and 38°F, away from temperature fluctuations.
Use breathable materials like wax paper or cheese paper for wrapping, and avoid airtight containers. Place cheese away from the refrigerator door and strong-smelling foods. Regularly inspect your cheese for any signs of mold, discoloration, or off-odors.
Consider freezing hard cheeses for extended storage but be aware of potential texture and flavor changes. By following these simple tips, you can reduce food waste, save money, and savor the full flavor of your cheese.